Cluster Mempool1 is an entire remodeling of how the mempool handles organizing and sorting transactions, conceptualized and carried out by Suhas Daftuar and Pieter Wuille. The design goals to simplify the general structure, higher align transaction sorting logic with miner incentives, and enhance safety for second layer protocols. It was merged into Bitcoin Core in PR #336292 on November 25, 2025.
The mempool is a huge set of pending transactions that your node has to maintain monitor of for a lot of causes: payment estimation, transaction alternative validation, and block development for those who’re a miner.
This can be a lot of various targets for a single operate of your node to service. Bitcoin Core as much as model 30.0 organizes the mempool in two other ways to assist help in these features, each from the relative viewpoint of any given transaction: mixed feerate trying ahead of the transaction and its kids (descendant feerate), and mixed feerate trying backwards of the transaction and its mother and father (ancestor feerate).
These are used to resolve which transactions to evict out of your mempool when it’s full, and which to incorporate first when establishing a brand new block template.
How Is My Mempool Managed?
When a miner is deciding whether or not to incorporate a transaction of their block, their node appears at that transaction, and any ancestors that should be confirmed first for it to be legitimate in a block, and take a look at the common feerate per byte throughout all of them collectively contemplating the person charges they paid as an entire. If that group of transactions matches throughout the blocksize restrict whereas outcompeting others in charges, it’s included within the subsequent block. That is finished for each transaction.
When your node is deciding which transactions to evict from its mempool when it’s full, it appears at every transaction and any kids it has, evicting the transaction and all its kids if the mempool is already full with transactions (and their descendants) paying the next feerate.
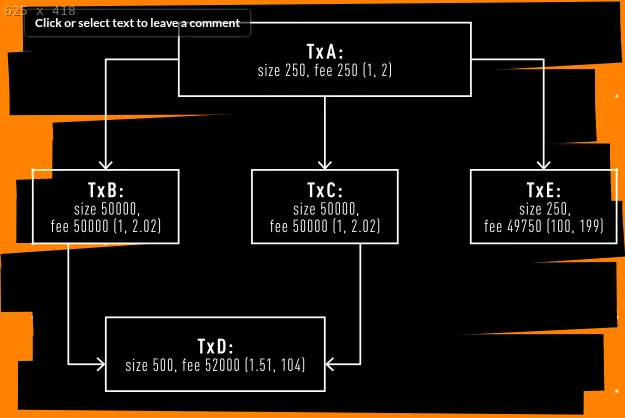
Take a look at the above instance graph of transactions, the feerates are proven as such in parentheses (ancestor feerate, descendant feerate). A miner transaction E would seemingly embody it within the subsequent block, a small transaction paying a really excessive payment with a single small ancestor. Nevertheless, if a node’s mempool was filling up, it could take a look at transaction A with two huge kids paying a low relative payment, and sure evict it or not settle for and maintain it if it was simply acquired.
These two rankings, or orderings, are fully at odds with one another. The mempool ought to reliably propagate what miners will mine, and customers must be assured that their native mempool precisely predicts what miners will mine.
The mempool functioning on this manner is necessary for:
- Mining decentralization: getting all miners essentially the most worthwhile set of transactions
- Consumer reliability: correct and dependable payment estimation and transaction affirmation instances
- Second layer safety: dependable and correct execution of second layer protocols’ on-chain enforcement transactions
The present conduct of the mempool doesn’t absolutely align with the fact of mining incentives, which creates blind spots that may be problematic for second layer safety by creating uncertainty as as to if a transaction will make it to a miner, in addition to stress for personal broadcasting channels to miners, doubtlessly worsening the primary drawback.
That is particularly problematic in relation to changing unconfirmed transactions, both merely to incentivize miners to incorporate a alternative sooner, or as a part of a second layer protocol being enforced on-chain.
Substitute per the present conduct turns into unpredictable relying on the form and dimension of the net of transactions yours is caught in. In a easy fee-bumping scenario this will fail to propagate and exchange a transaction, even when mining the alternative could be higher for a miner.
Within the context of second layer protocols, the present logic permits contributors to doubtlessly get essential ancestor transactions evicted from the mempool, or make it not doable for an additional participant to submit a essential youngster transaction to the mempool beneath the present guidelines due to youngster transactions the malicious participant created, or the eviction of essential ancestor transactions.
All of those issues are the results of these inconsistent inclusion and eviction rankings and the motivation misalignments they create. Having a single international rating would repair these points, however globally reordering the whole mempool for each new transaction is impractical.
It’s All Simply A Graph
Transactions that rely on one another are a graph, or a directed sequence of “paths.” When a transaction spends outputs created by one other up to now, it’s linked with that previous transaction. When it moreover spends outputs created by a second previous transaction, it hyperlinks each of the historic transactions collectively.
When unconfirmed, chains of transactions like this should have the sooner transactions confirmed first for the later ones to be legitimate. In spite of everything, you’ll be able to’t spend outputs that haven’t been created but.
This is a vital idea for understanding the mempool, it’s explicitly ordered directionally.
It’s all only a graph.
Chunks Make Clusters Make Mempools
In cluster mempool, the idea of a cluster is a bunch of unconfirmed transactions which are immediately associated to one another, i.e. spending outputs created by others within the cluster or vice versa. This turns into a elementary unit of the brand new mempool structure. Analyzing and ordering the whole mempool is an impractical job, however analyzing and ordering clusters is a way more manageable one.
Every cluster is damaged down into chunks, small units of transactions from the cluster, that are then sorted so as of highest feerate per byte to lowest, respecting the directional dependencies. So as an example, let’s say from highest to lowest feerate the chunks in cluster (A) are: [A,D], [B,E], [C,F], [G, J], and final [I, H].
This enables pre-sorting all of those chunks and clusters, and extra environment friendly sorting of the entire mempool within the course of.
Miners can now merely seize the very best feerate chunks from each cluster and put them into their template, if there may be nonetheless room they’ll go right down to the following highest feerate chunks, persevering with till the block is roughly full and simply wants to determine the previous couple of transactions it may match. That is roughly the optimum block template development technique assuming entry to all accessible transactions.
When nodes’ mempools get full, they’ll merely seize the bottom feerate chunks from each cluster, and begin evicting these from their mempool till it’s not over the configured restrict. If that was not sufficient, it strikes on to the following lowest feerate chunks, and so forth, till it’s inside its mempool limits. Performed this manner it removes unusual edge circumstances out of alignment with mining incentives.
Substitute logic can also be drastically simplified. Examine cluster (A) to cluster (B) the place transaction Ok has changed G, I, J, and H. The one standards that must be met is the brand new chunk [K] should have the next chunk feerate than [G, J] and [I, H], [K] should pay extra in whole charges than [G, J, I, H], and Ok can’t go over an higher restrict of what number of transactions it’s changing.
In a cluster paradigm all of those completely different makes use of are in alignment with one another.
The New Mempool
This new structure permits us to simplify transaction group limits, eradicating earlier limitations on what number of unconfirmed ancestors a transaction within the mempool can have and changing them with a world cluster restrict of 64 transactions and 101 kvB per cluster.
This restrict is critical in an effort to maintain the computational price of pre-sorting the clusters and their chunks low sufficient to be sensible for nodes to carry out on a relentless foundation.
That is the true key perception of cluster mempool. By conserving the chunks and clusters comparatively small, you concurrently make the development of an optimum block template low-cost, simplify transaction alternative logic (fee-bumping) and due to this fact enhance second layer safety, and repair eviction logic, .
No costlier and gradual on the fly computation for template constructing, or unpredictable conduct in fee-bumping. By fixing the misalignment of incentives in how the mempool was managing transaction group in several conditions, the mempool features higher for everybody.
Cluster mempool is a undertaking that has been years-long within the making, and can make a fabric influence on making certain worthwhile block templates are open to all miners, that second layer protocols have sound and predictable mempool behaviors to construct on, and that Bitcoin can proceed functioning as a decentralized financial system.
For these attention-grabbing in diving deeper into the nitty gritty of how cluster mempool is carried out and works beneath the hood, listed here are two Delving Bitcoin threads you’ll be able to learn:
Excessive Degree Implementation Overview (With Design Rationale): https://delvingbitcoin.org/t/an-overview-of-the-cluster-mempool-proposal/393
How Cluster Mempool Feerate Diagrams Work: https://delvingbitcoin.org/t/mempool-incentive-compatibility/553
Don’t miss your likelihood to personal The Core Situation — that includes articles written by many Core Builders explaining the initiatives they work on themselves!
This piece is the Letter from the Editor featured within the newest Print version of Bitcoin Journal, The Core Situation. We’re sharing it right here as an early take a look at the concepts explored all through the complete challenge.
[1] https://github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin/points/27677
[2] https://github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin/pull/33629